OpenAI, Inc., best known for developing ChatGPT, has a board of directors who oversee its nonprofit entity. They represent shareholders' interests when making pivotal decisions regarding an organization's policy, strategy, and finances.
Nonprofit organizations such as OpenAI, Inc. operate for charitable, educational, or similar purposes, with any profits reinvested to advance the organization's mission.
OpenAI, Inc. uses governance as an umbrella term to cover its broad decision-making and oversight responsibilities for its organization's nonprofit and for-profit sectors. At the same time, OpenAI's board oversees these divisions separately from their daily management and operations.
OpenAI, Inc. exercises sole control over OpenAI LP through OpenAI GP LLC - serving as its general partner responsible for overseeing management.
OpenAI LP is responsible for OpenAI's for-profit ventures while being overseen by OpenAI Inc. in such a way as to match it with its overall mission while operating under an established structure. OpenAI LP operates under a capped profit structure designed to ensure profits do not outstrip the ethical and safety-oriented objectives of OpenAI Inc.
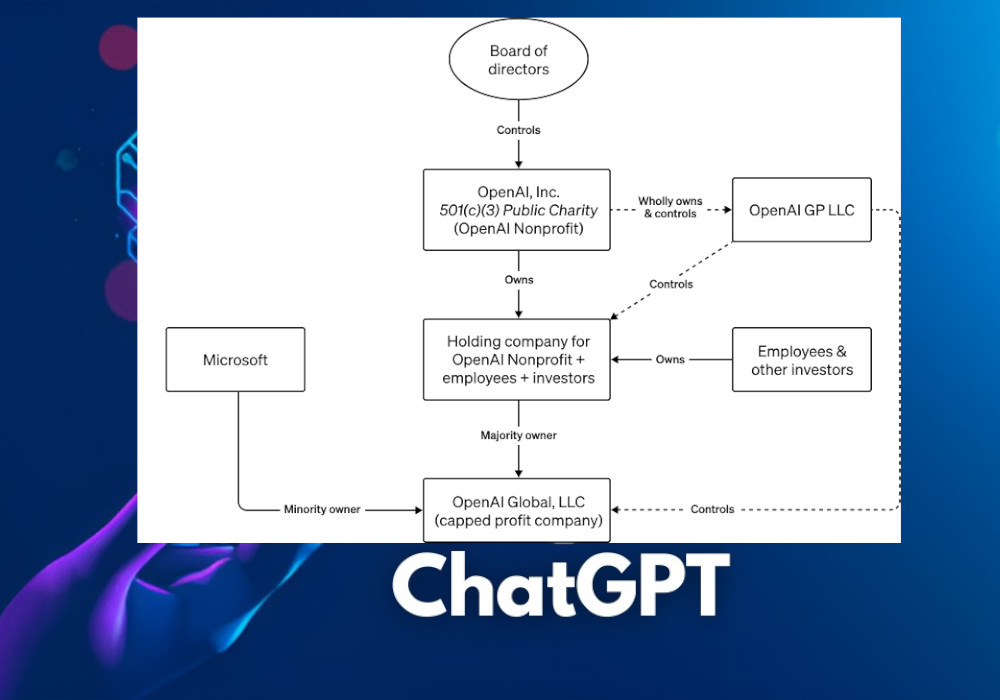
Who Really Owns Control of This Complex Corporate Structure?
OpenAI, Inc. is the ultimate governing body within its company structure, holding ultimate authority to set the mission, policies, and strategic direction of OpenAI, including its for-profit arm, OpenAI LP.
However, power dynamics in such an arrangement can be complex and shifting when considering both mission-driven aspects of nonprofit operations and the profit motives of for-profit units.
Nonprofit Control: OpenAI, Inc. maintains control over its for-profit activities through OpenAI LP to ensure they align with its broader mission and ethical guidelines, with board decisions having significant ramifications on both arms of the organization.
Operational Independence: OpenAI LP's independence allows it to respond more flexibly and responsively when handling for-profit operations; however, its operational independence also creates potential areas of contention where power imbalance could arise if for-profit motives diverge significantly from the nonprofit mission.
Capped Profit Structure of OpenAI LP: Our capped profit structure serves an integral purpose: aligning profit motives with the ethical goals of a nonprofit. However, its implementation may seriously impact power balance; too lax enforcement might prioritize profit over mission; too restrictive might prevent essential investment and growth.
Investor Influence: Outside investors like Microsoft that have invested in OpenAI LP are interested in its financial success. While their influence might not be as pronounced as traditional corporate structures, investor pressures and expectations may still influence operational decisions and priorities that impact the nonprofit and thus challenge its guiding principles.
OpenAI faces considerable public and regulatory scrutiny as an AI research entity, serving as a check on nonprofit and for-profit arms that do not adhere to stated missions and ethical standards—such scrutiny checks against abuses within their mission statement or code of ethics.
As is evident from this structure, while OpenAI Inc.'s board of directors holds ultimate control, their balance of power is maintained through operational independence, capped profit structures, investor influence, and external scrutiny. Maintaining this delicate equilibrium requires ongoing attention to ensure for-profit activities are consistent with nonprofit mission and ethical standards.

